Precision in Power: Mastering Digital Power Control

Introduction
Digital Power Control is revolutionizing the way we manage and optimize electrical systems. This article explores the transformative impact of digital control technologies in power systems, delving into the key principles, applications, and advantages that make it a pivotal advancement in the field.
To delve deeper into Digital Power Control, visit here. This resource offers additional insights and resources on the applications and benefits of Digital Power Control in various industries.
Understanding Digital Power Control
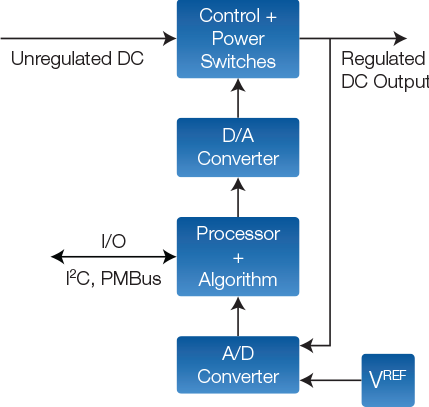
At its core, Digital Power Control involves the use of digital technologies to regulate and manage electrical power. This section provides a foundational understanding of digital control principles, highlighting the shift from analog to digital methods in power system management. The precision and adaptability of digital control set it apart from traditional analog approaches.
Applications in Power Electronics
Digital Power Control finds extensive applications in power electronics. This section explores how digital controllers are employed in converters, inverters, and motor drives. The flexibility of digital systems allows for advanced control algorithms, enabling precise regulation of voltage, current, and frequency in various power electronic devices.
Advantages of Digital Power Control
The advantages of Digital Power Control are multifaceted. This section outlines the key benefits, including enhanced accuracy, faster response times, adaptability to varying loads, and the ability to implement complex control strategies. Digital control’s efficiency and reliability make it a game-changer in optimizing power systems.
Integration of Digital Signal Processors (DSP)
Digital Signal Processors (DSP) play a pivotal role in Digital Power Control. This section explores how DSPs are integrated into power control systems, enabling real-time processing of signals and execution of sophisticated control algorithms. The integration of DSPs enhances the computational capabilities of digital controllers.
To explore more about the integration of Digital Signal Processors in Digital Power Control, visit here. This resource provides additional insights into the role of DSPs in advancing power control technologies.
Implementing Digital Control in Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems benefit significantly from Digital Power Control. This section discusses how digital control optimizes the performance of solar inverters, wind turbine controllers, and other renewable energy devices. The adaptability of digital systems allows for efficient energy harvesting and grid integration.
Digital Power Control in Grid-Tied Systems
In grid-tied power systems, precise control is essential for stability and efficiency. This section explores how digital control contributes to grid-tied systems, including smart grids. The ability to monitor and adjust parameters in real-time enhances the reliability of power distribution and facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources.
Challenges and Solutions
While Digital Power Control offers numerous advantages, it comes with its set of challenges. This section examines common challenges such as cybersecurity concerns, system complexity, and the need for skilled personnel. Solutions and strategies to address these challenges are discussed, emphasizing the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and continuous education.
Industry 4.0 and Digital Power Control
Digital Power Control aligns seamlessly with the principles of Industry 4.0. This section explores how Industry 4.0, characterized by the integration of digital technologies in manufacturing, benefits from advanced power control systems. The synergy between digital power control and Industry 4.0 enhances overall operational efficiency and energy management in industrial settings.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of Digital Power Control holds exciting possibilities. This section explores emerging trends and innovations, including the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and edge computing in power control systems. These advancements promise even greater levels of automation, adaptability, and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Digital Power Control stands as a transformative force in the realm of electrical systems. From power electronics to renewable energy and Industry 4.0, the applications are diverse and impactful. As technology continues to evolve, Digital Power Control will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the efficiency and sustainability of power systems worldwide.








